Introduction
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as the foundation for modern electronic devices, providing essential support and connectivity for various components. A critical aspect of PCB design and manufacturing is PCB board thickness. In this article, we will explore what PCB thickness is, why it matters, and how to select the right thickness for your specific applications.
What Are the Standard PCB Thicknesses?
Common Thickness Measurements
PCB thickness is typically measured in millimeters (mm) or inches. The most common standard thicknesses include:
- 0.4 mm (15 mils)
- 0.6 mm (24 mils)
- 1.0 mm (40 mils)
- 1.6 mm (63 mils)
- 2.0 mm (79 mils)
These measurements represent the total thickness of the PCB, including the substrate and copper layers.
Which Industry Standards Influence PCB Thickness?
The electronics industry adheres to specific standards that influence PCB thickness choices. Organizations such as IPC/JPCA and UL provide guidelines that manufacturers follow to ensure quality and reliability. Familiarizing yourself with these standards can help you make informed decisions about your PCB designs.
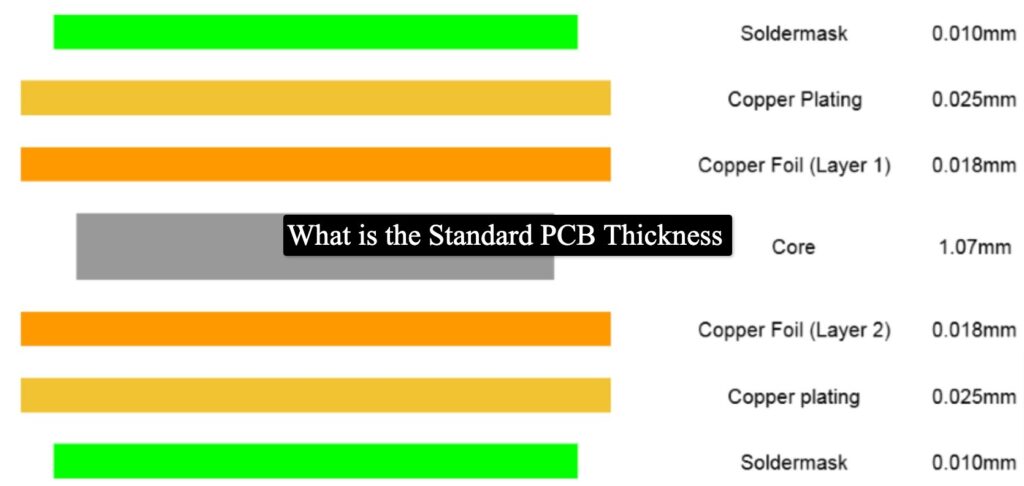
What Factors Influence PCB Thickness?
Substrate Material
The choice of substrate material significantly impacts PCB thickness. Common materials include:
- FR4: A popular fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate known for its mechanical strength and versatility.
- Polyimide: Valued for its thermal stability, often used in flexible PCBs.
Each material has distinct properties that affect the overall thickness and performance of the PCB.
How Does Copper Thickness Affect Performance?
Copper thickness is measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²) and plays a crucial role in electrical performance:
- 1 oz/ft²: Commonly used for standard applications.
- 2 oz/ft² or more: Suitable for high-current applications, providing better conductivity but increasing overall thickness.
How Does Layer Count Impact Thickness?
The number of layers in a PCB directly affects its thickness. Single-layer boards are thinner than multi-layer boards, which can range from two to more than ten layers, depending on complexity and design requirements.

What Are the Applications Based on Thickness?
Ultra-Thin PCBs (Below 0.6mm)
Ultra-thin PCBs are perfect for compact devices such as smartphones, wearables, and IoT gadgets where space is at a premium. These boards often utilize advanced materials and technologies to maintain performance while minimizing size.
Mid-Range PCBs (0.6mm – 1.6mm)
Mid-range PCBs are versatile and suitable for most consumer electronics, including laptops, tablets, and household appliances. This thickness range strikes a balance between durability and functionality.
Thicker PCBs (Above 1.6mm)
Thicker PCBs are commonly used in industrial controls, automotive applications, and high-power devices where mechanical strength and thermal management are critical. These boards can handle higher currents and provide better heat dissipation.
How Do You Choose the Right Thickness?
Key Design Considerations
When selecting PCB thickness, consider the following factors:
- Application Requirements: Assess the specific needs of your device.
- Space Constraints: Evaluate how much space you have available for the PCB.
- Thermal Management: Determine if your application requires enhanced heat dissipation.
What Are the Performance Trade-offs?
Selecting the appropriate thickness involves understanding trade-offs:
- Signal Integrity: Thicker boards may offer better signal integrity due to increased copper area but can also lead to increased capacitance.
- Mechanical Strength: Thicker boards provide greater mechanical support but may be less flexible.
What Are Future Trends in PCB Thickness?
Advancements in Materials
As technology evolves, new materials are being developed that allow for thinner yet more durable PCBs. Innovations such as high-frequency laminates and flexible substrates pave the way for more compact designs without compromising performance.
How Is Market Demand Shaping PCB Design?
The demand for smaller, lighter electronic devices continues to rise, driving manufacturers to explore varying thicknesses in their designs. Staying informed about market trends can help you remain competitive in PCB design and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Understanding PCB board thickness is essential for anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing. By considering factors such as substrate material, copper thickness, layer count, and application requirements, you can make informed decisions that enhance your product’s performance and reliability.
If you’re looking to optimize your PCB designs or have specific questions about selecting the right thickness for your project, reach out to our team of experts today! We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of PCB manufacturing and ensure your success in this ever-evolving industry.