Ceramic PCB material is rapidly gaining traction in industries requiring high-performance circuit boards capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Unlike traditional FR4 or metal-based PCBs, ceramic PCBs offer unique advantages, such as exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and durability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what ceramic PCB material is, its key benefits, common applications, and critical manufacturing considerations to help you decide if it’s the right choice for your next project.
What Is Ceramic PCB Material?
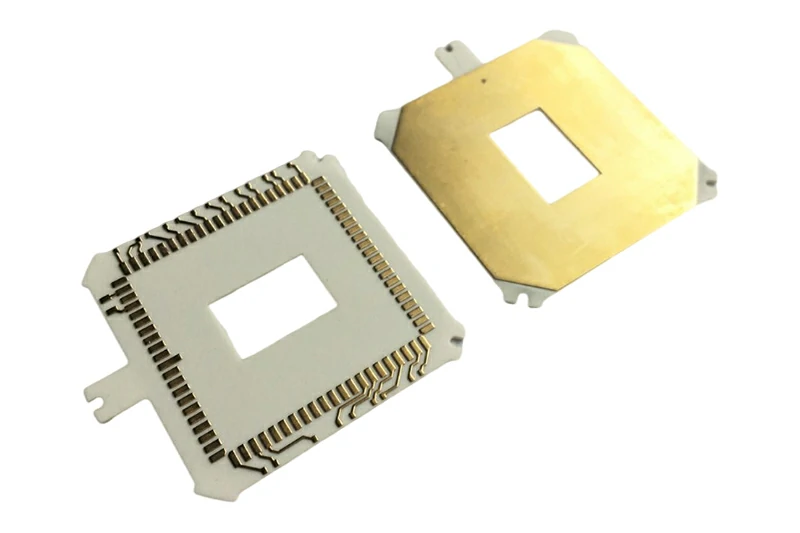
Ceramic PCB material refers to printed circuit boards that use ceramic substrates, such as aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlN), or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), instead of conventional materials like fiberglass or epoxy resin. These substrates are paired with conductive layers, typically copper, to create a robust and thermally efficient circuit board.
Unlike standard PCBs, ceramic PCB material is designed to handle high temperatures, high-frequency signals, and demanding environments. Its inorganic composition makes it resistant to moisture, corrosion, and thermal expansion, setting it apart from organic-based alternatives like FR4.
Types of Ceramic Substrates
- Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃): The most common and cost-effective option, offering good thermal conductivity (20-30 W/m·K) and electrical insulation.
- Aluminum Nitride (AlN): Known for its superior thermal conductivity (up to 170-200 W/m·K), ideal for high-power applications.
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): Offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, though it’s less common due to higher costs.
Each type of ceramic PCB material caters to specific needs, making it essential to choose the right substrate based on your project’s thermal, electrical, and mechanical requirements.
Why Choose Ceramic PCB Material? Key Benefits Explained
Ceramic PCBs stand out for their ability to meet the demands of advanced electronics. Here are the primary benefits that make them a preferred choice:
Exceptional Thermal Management
One of the standout features of ceramic PCB material is its high thermal conductivity. For instance, aluminum nitride can dissipate heat up to 10 times more effectively than FR4. This makes ceramic PCBs ideal for applications like high-power LED lighting or automotive systems where heat dissipation is critical.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Ceramic substrates provide excellent dielectric strength, ensuring minimal signal loss and reliable performance in high-voltage environments. This is particularly valuable in radar systems or medical instruments requiring precision.
Durability and Reliability
Thanks to their resistance to corrosion, moisture, and thermal cycling, ceramic PCBs maintain performance over time, even in harsh conditions like industrial control systems or aerospace applications.
High-Frequency Performance
The low dielectric constant and loss tangent of ceramic PCB material make it perfect for high-frequency and high-speed circuits, such as those in telecommunications or computer peripherals.
Compact Design Potential
Ceramic PCBs support high-density interconnect (HDI) designs, allowing for smaller, more efficient layouts without sacrificing performance—a key advantage in modern miniaturized electronics.
Applications of Ceramic PCB Material
The unique properties of ceramic PCB material make it a go-to solution across various industries. Here are some of its most common applications:
High-Power LED Lighting
Ceramic PCBs efficiently dissipate heat generated by high-power LEDs, ensuring longevity and performance in lighting systems for homes, streets, or automotive use.
Automotive Electronics
From battery management systems (BMS) to radar and lighting, ceramic PCBs handle the heat and vibration challenges of automotive environments with ease.
Medical Devices
In medical instruments like imaging equipment or sensors, ceramic PCB material ensures precision and reliability under stringent conditions.
Industrial Systems
Industrial detection and control systems benefit from ceramic PCBs’ ability to operate in high-temperature or corrosive settings.
Aerospace and Defense
Ceramic PCBs’ durability and high-frequency capabilities make them essential for radar, communication devices, and other aerospace technologies.
Manufacturing Ceramic PCBs: Key Considerations
Producing ceramic PCBs requires specialized expertise and equipment due to the material’s unique properties. Here’s what goes into the process:
Material Selection
Choosing the right ceramic substrate is critical. For example, AlN is preferred for high-heat applications, while Al₂O₃ suits cost-sensitive projects. Pairing the substrate with high-quality copper layers ensures optimal conductivity.
Advanced Production Techniques
Manufacturing ceramic PCBs involves precise processes like laser drilling for vias, thick-film or thin-film technology for circuit patterns, and sintering to bond layers. Equipment such as LDI exposure machines and automated plating lines ensures accuracy and consistency.
Thermal and Electrical Testing
To guarantee performance, ceramic PCBs undergo rigorous testing, including impedance testing, X-ray inspection, and thermal cycling. These tests verify the board’s ability to handle heat and maintain signal integrity.
Challenges in Manufacturing
Ceramic PCB material is brittle compared to FR4, requiring careful handling during production. Additionally, its higher cost can be a barrier for low-budget projects, though the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Ceramic PCB Material vs. Metal Base PCBs: A Comparison
While ceramic PCBs excel in thermal and electrical performance, how do they stack up against metal base PCBs (like aluminum or copper)? Let’s break it down:
- Thermal Conductivity: Ceramic PCBs (e.g., AlN) often outperform aluminum-based PCBs, though copper-based options like SinkPAD PCBs offer competitive heat dissipation.
- Weight: Metal base PCBs are heavier, while ceramic PCBs are lighter, benefiting weight-sensitive applications.
- Cost: Metal base PCBs are generally more affordable, but ceramic PCBs justify their price in high-performance scenarios.
- Flexibility: Metal base PCBs can be adapted for thermoelectric separation designs (e.g., SinkPAD), while ceramic PCBs are rigid but excel in HDI applications.
Both options have their place, but ceramic PCB material shines in extreme conditions requiring top-tier thermal and electrical properties.
Tips for Choosing Ceramic PCB Material for Your Project
When considering ceramic PCBs, keep these factors in mind:
- Define Your Thermal Needs: Assess the heat dissipation requirements of your application to select the right substrate.
- Evaluate Frequency Demands: For high-speed or high-frequency designs, prioritize materials with low dielectric loss.
- Budget Wisely: Balance upfront costs with long-term performance benefits.
- Partner with Experts: Work with a manufacturer experienced in ceramic PCB production to ensure quality and reliability.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Potential of Ceramic PCB Material
Ceramic PCB material offers a powerful solution for industries pushing the boundaries of thermal management, electrical performance, and durability. Whether you’re designing high-power LED systems, automotive electronics, or cutting-edge medical devices, ceramic PCBs provide the reliability and efficiency needed to succeed. While they come with a higher initial cost and manufacturing complexity, their long-term advantages make them a worthwhile investment for demanding applications.
At TriWin PCB, we specialize in delivering advanced PCB solutions tailored to your needs. With over a decade of experience and a commitment to quality—backed by certifications like ISO9001 and IATF16949—we’re equipped to support your ceramic PCB projects with precision and expertise. Contact us today to explore how we can help bring your designs to life with reliable, high-performance circuit boards.