Introduction
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the unsung heroes of modern electronics, quietly powering everything from your smartphone to sophisticated spacecraft. These intricate boards connect and support the components that make our devices tick. But if you’ve ever peeked inside an electronic gadget, you might have noticed something intriguing: PCBs come in a variety of colors. While green is the most familiar, you’ll also find boards in blue, red, black, white, and even more exotic shades like yellow or purple. So, what’s behind this rainbow of options? Does the color of a PCB affect its performance, or is it just a cosmetic choice? In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the world of PCB colors, uncovering the reasons for their diversity, debunking myths, and examining what these choices mean for manufacturers, designers, and consumers. By the end, you’ll see that there’s more to PCB colors than meets the eye!
The Diversity of PCB Colors
PCBs aren’t limited to a single hue—they come in an array of colors, each with distinct characteristics and uses. Here’s a rundown of the most common PCB colors and what makes them special:
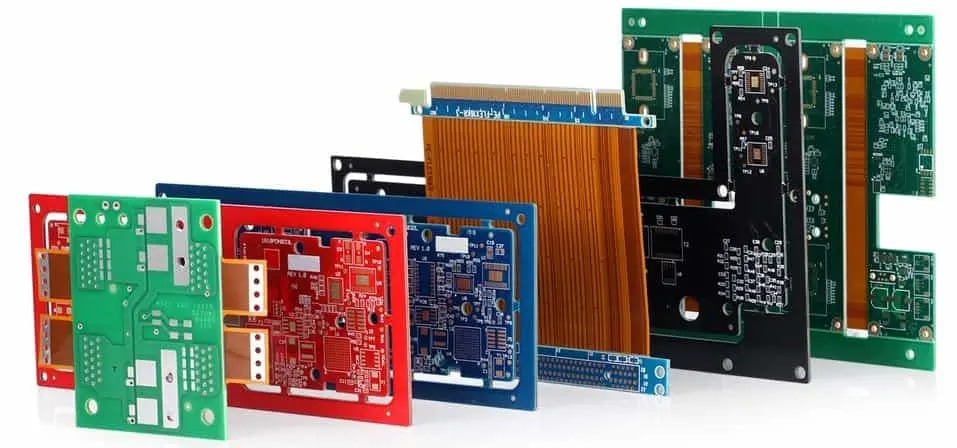
Common PCB Colors
- Green: The undisputed champion of PCB colors, green has been the industry standard for decades. Its popularity stems from its high contrast, which makes it easy to inspect the copper traces and solder joints for defects. Green PCBs are a staple in everything from industrial equipment to consumer gadgets.
- Blue: A favorite in modern electronics, blue PCBs offer a sleek, contemporary look. They’re often seen in devices where aesthetics matter, like audio equipment or custom-built PCs. While blue doesn’t provide the same inspection clarity as green, it’s a stylish alternative.
- Red: Bold and vibrant, red PCBs stand out and are frequently chosen for branding purposes. A company might opt for red to match their logo or product design, turning the PCB into a visual statement. You might spot them in automotive electronics or eye-catching consumer products.
- Black: Exuding a premium vibe, black PCBs are common in high-end devices like gaming consoles or luxury gadgets. The dark color can make inspection trickier, but its sophisticated appearance often outweighs that drawback in design-focused applications.
- White: White PCBs shine—literally—in LED lighting applications. The reflective solder mask enhances brightness and efficiency, making white a go-to choice for light fixtures and displays.
- Other Colors: Beyond the staples, PCBs can be yellow, purple, or even custom shades. These are less common but might be used for niche projects, prototypes, or to differentiate a product in a competitive market.
Each color brings its own flair, balancing practicality with visual appeal. But why do PCBs come in different colors at all? Let’s dive into the manufacturing process to find out.
Why PCBs Come in Different Colors
The secret to a PCB’s color lies in the solder mask, a thin polymer layer applied during manufacturing. This layer isn’t just for show—it serves critical functions:
- Protection: It prevents solder from bridging between conductors, avoiding short circuits during assembly.
- Insulation: It provides electrical insulation between copper traces.
- Durability: It shields the copper from oxidation, ensuring the board lasts longer.
The solder mask’s color is determined by pigments mixed into the polymer before it’s applied to the PCB. Green became the default because it’s cost-effective and offers excellent visibility. The green hue contrasts sharply with the copper traces and white silkscreen (used for labeling), making it a technician’s dream for spotting defects.

But manufacturers aren’t limited to green. They can produce solder masks in virtually any color by adjusting the pigments. So why isn’t every PCB a different shade? Here are the key reasons for color variation:
- Cost and Standardization: Green solder masks are the cheapest and most standardized, thanks to decades of mass production. Other colors might require special formulations or additional processing, slightly increasing costs.
- Customer Preference: Some clients request specific colors for branding or design consistency. For example, a tech startup might choose blue PCBs to match their sleek product aesthetic.
- Functional Needs: In rare cases, color ties to functionality. White PCBs reflect light in LED setups, while high-frequency boards might (theoretically) use certain colors to minimize signal interference—though this is uncommon.
At TriWin PCB, we recognize that every project has unique demands. That’s why we offer a spectrum of solder mask colors, ensuring our clients get both the performance and style they need. But does this color choice actually change how a PCB works? Let’s tackle that next.
Does Color Affect PCB Performance?
One question often pops up: does a PCB’s color impact its performance? The short answer is no. The electrical properties of a PCB—think signal integrity, impedance, and heat dissipation—depend on the materials (like the substrate and copper) and the design (trace layout, layer stackup), not the solder mask’s color. A red PCB won’t conduct electricity any differently than a green one.
That said, there are a few indirect effects to consider:
- Inspection Ease: Colors like green or yellow provide high contrast, making it simpler to spot defects during quality control. Darker colors like black can obscure traces, potentially complicating manual inspection. This doesn’t affect performance but can influence manufacturing reliability.
- Heat Absorption: Darker solder masks (e.g., black) absorb more heat than lighter ones (e.g., white). In theory, this could raise the board’s temperature slightly. In practice, though, the difference is so small it rarely matters, even in high-power applications.
- Specialized Applications: White PCBs reflect light better, boosting efficiency in LED systems. This isn’t about electrical performance but rather optimizing the device’s intended function.
Let’s debunk a myth while we’re at it: some believe green PCBs are “better” because they’re so common. Not true! Green’s dominance is a historical fluke—early solder masks were green due to available materials, and it stuck because it worked well for inspection and cost. Other colors perform just as well when made to the same standards.
At TriWin PCB, we ensure every board—green, blue, or beyond—meets rigorous quality benchmarks. Our advanced manufacturing and testing processes guarantee top-notch performance, no matter the color.
Factors Customers Consider When Choosing PCB Colors
So, if color doesn’t affect performance, why bother choosing? Customers weigh several factors when picking a PCB hue:
- Cost: Green PCBs are the budget-friendly option due to their standardized production. Opting for blue, black, or custom colors might add a small premium—usually worth it for the right project.
- Aesthetics: In devices where the PCB is visible (think transparent cases or open-frame designs), looks matter. A vibrant red or matte black PCB can elevate a product’s appeal, aligning with brand identity or consumer trends.
- Functionality: Certain colors serve practical purposes:
- Inspection: High-contrast colors like green or yellow simplify quality checks.
- Application-Specific Needs: White for LEDs, black for a premium feel.
- Branding: A company might choose purple PCBs to match their logo, reinforcing their visual identity.
- Industry Trends: As electronics blend with fashion and lifestyle, unique PCB colors are gaining traction. Designers use them to stand out or signal innovation, especially in competitive markets like wearables or gaming.
- Availability: While most manufacturers offer a range of colors, rare shades might require custom orders, affecting lead times or costs.
At TriWin PCB, we collaborate with clients to find the perfect balance. Need a cost-effective green board for a high-volume run? We’ve got you. Want a custom yellow PCB for a standout prototype? We’ll make it happen. Our expertise ensures you get a board that fits your budget, vision, and technical specs.
Conclusion
PCB colors may seem like a small detail, but they weave together manufacturing history, customer creativity, and practical considerations. While the solder mask’s hue doesn’t alter a board’s electrical performance, it can influence cost, inspectability, and aesthetics—factors that matter just as much in the right context. Green remains the king for its affordability and clarity, but the rise of customization means blue, red, black, and beyond are carving out their own space.
When planning your next PCB project, think about what drives your decision. Prioritizing efficiency and cost? Stick with green. Aiming to dazzle with design? Explore the palette. At TriWin PCB, we’re here to turn your ideas into reality, offering high-quality boards in any color you choose. So, next time you spot a colorful PCB inside your favorite gadget, you’ll know it’s not just a circuit—it’s a story of innovation and choice.
FAQs
Q: Why is green the most common PCB color?
A: Green took the lead thanks to its high contrast for inspection and low production cost. It’s been the standard since the early days of PCB manufacturing.
Q: Can I choose any color for my PCB?
A: Absolutely! Most manufacturers, like TriWin PCB, offer a variety of colors. Custom shades might cost a bit more or take extra time, but the option’s there.
Q: Does PCB color affect heat dissipation?
A: Darker colors absorb more heat, but the difference is tiny and doesn’t meaningfully impact performance in most cases.
Q: Are there performance differences between PCB colors?
A: No, color doesn’t affect electrical properties. Performance hinges on materials and design, not the solder mask’s hue.
Q: How do I pick the right PCB color?
A: Consider your budget, design goals, and application needs. Green is great for cost and clarity; other colors shine for aesthetics or specific uses.